Measuring AAV genome length with mass photometry
In this application note – created in collaboration with AskBio – you will learn how mass photometry can be used to measure the encapsidated AAV genome length. The app note showcases how the SamuxMP and SamuxMP auto mass photometers easily detect and quantify empty and full AAV populations. You will also see example data from AAV samples of different serotypes showing expected vs measured AAV genome length, highlighting the precision of mass photometry.
Download the tech note
AAV genome length is a key analytical attribute for gene therapies
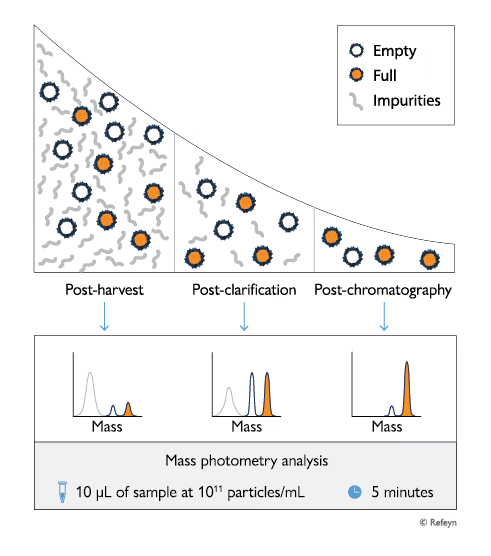
Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) are important therapeutic viral vectors frequently used in emerging gene therapies. AAVs are produced using transfected cell cultures. These production systems are not perfect and frequently produce capsids containing no genome, a partial genome or a longer-than-expected genome – likely due to the presence of plasmid impurities or genome fragments from the host cell.
Therefore, developing and producing safe and effective AAV-based gene therapies requires implementing robust analytical strategies that can efficiently and accurately characterize AAV quality. Monitoring critical quality attributes, including AAV genome length, enables early detection of potential issues during development and supports optimization of AAV quality in production workflows.
Mass photometry quickly and accurately assesses AAV quality
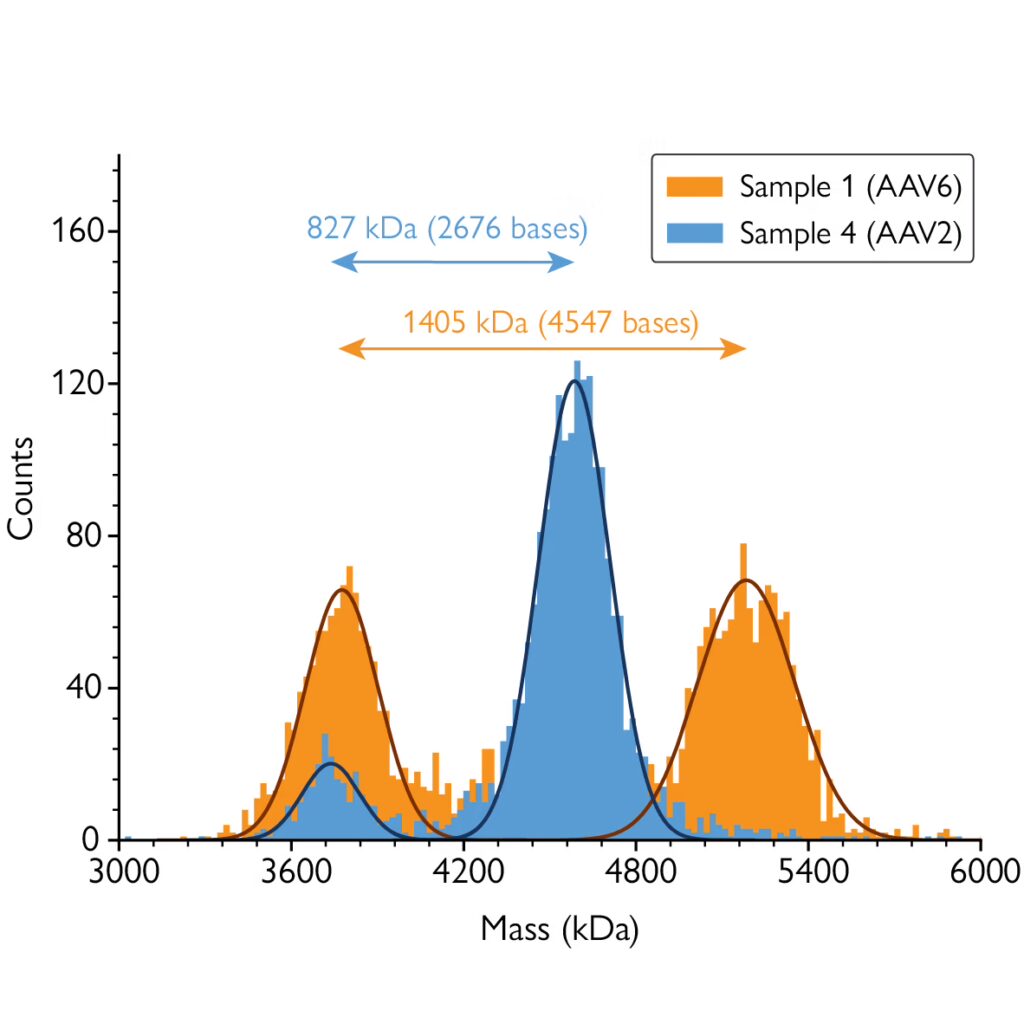
Mass photometry is a powerful analytical technology that measures the mass of AAVs in solution at the single-particle level. Mass photometry measurements take only a few minutes and consume very little sample, which makes it ideal for in-line, fast characterization of AAV quality. Mass photometry can easily detect and quantify different AAV populations – including empty, full and partially filled capsids – as well as measure their average masses.
From the data provided by mass photometry, AAV genome length can be easily quantified for each detected population. Its low turnaround times, low sample consumption and ease of use when compared to other techniques such as sedimentation velocity analytical ultracentrifugation (SV-AUC) make mass photometry an excellent technique to evaluate this key indicator of AAV quality.