Copolymer nanodiscs solubilize GPCRs
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are integral membrane proteins that fulfill essential biological roles and are frequent therapeutic targets.
As with other membrane proteins, GPCRs contain hydrophobic domains that disrupt the protein’s structure and activity in aqueous buffer. For this reason, membrane mimetics are used to solubilize and stabilize membrane proteins.
Composed of a lipid bilayer stabilized by a copolymer that encircles the lipids and membrane proteins, copolymer-derived nanodiscs enable the study of GPCRs and other membrane proteins without detergents.
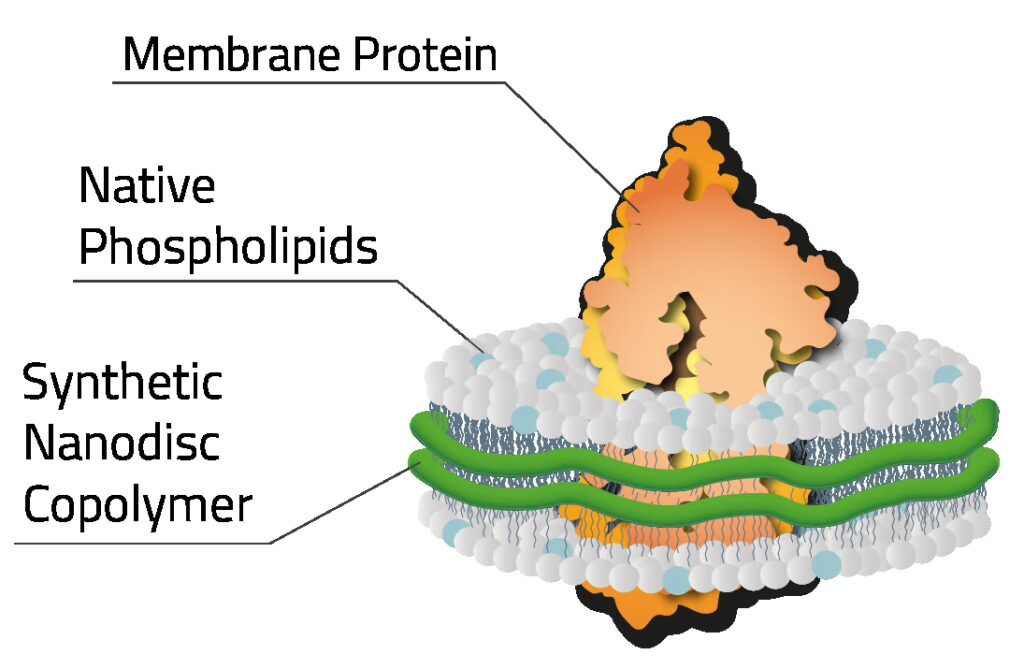
Mass photometry characterizes nanodisc-solubilized GPCRs
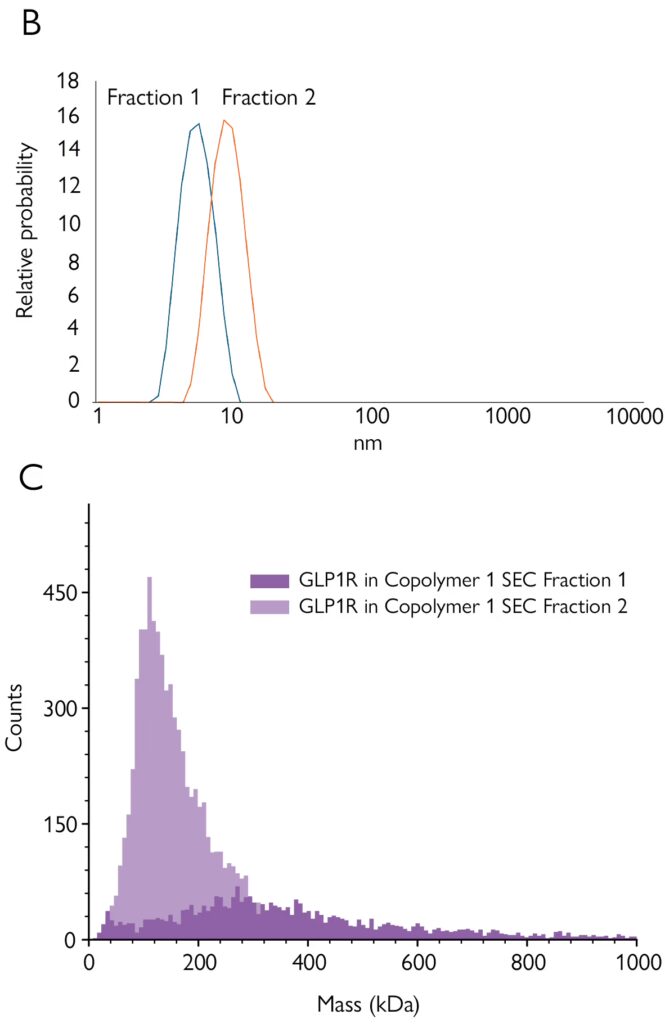
In this application note, created in collaboration with CUBE Biotech, copolymer-derived nanodiscs were used to solubilize GPCRs. The embedded proteins were fractionated using SEC, then characterized with SDS-PAGE, western blot, DLS and mass photometry.
Mass photometry characterized the SEC fractions quickly and with minimal sample preparation – providing a more detailed overview of the populations than other techniques. These advantages make mass photometry well-suited for efficient quality checks during membrane protein preparation prior to structural studies or functional assays.
Discover how mass photometry characterizes nanodisc-embedded GPCRs
Analysis of GPCRs in copolymer-derived nanodiscs with mass photometry
Discover how to use mass photometry to expedite functional assays or structural investigations by obtaining detailed information on your membrane protein samples or SEC fractions. Learn how copolymer-derived nanodiscs can be used for GPCR solubilization, and how mass photometry compares to other techniques in this context.
Additional resources on mass photometry analysis of membrane proteins
WEBINAR: Investigating membrane protein complexes with mass photometry
This webinar shows the applications of mass photometry for the study of two examples of macromolecular complexes formed by eukaryotic membrane proteins. In both cases, mass photometry was crucial to addressing highly relevant physiological questions. The webinar showcases what value can mass photometry deliver, and what makes it suitable for studies of membrane protein complexes.


BLOG: How to study membrane proteins with mass photometry
Mass photometry provides valuable information on the purity and behavior of samples containing membrane proteins and membrane mimetics. In this blog post, we examine the role of mass photometry in membrane protein analysis and describe case studies that illustrate how mass photometry is contributing to the field.
To implement mass photometry in your membrane protein research
More Application Notes
Browse through our catalogue of application notes highlighting some recent case studies featuring mass photometry.
