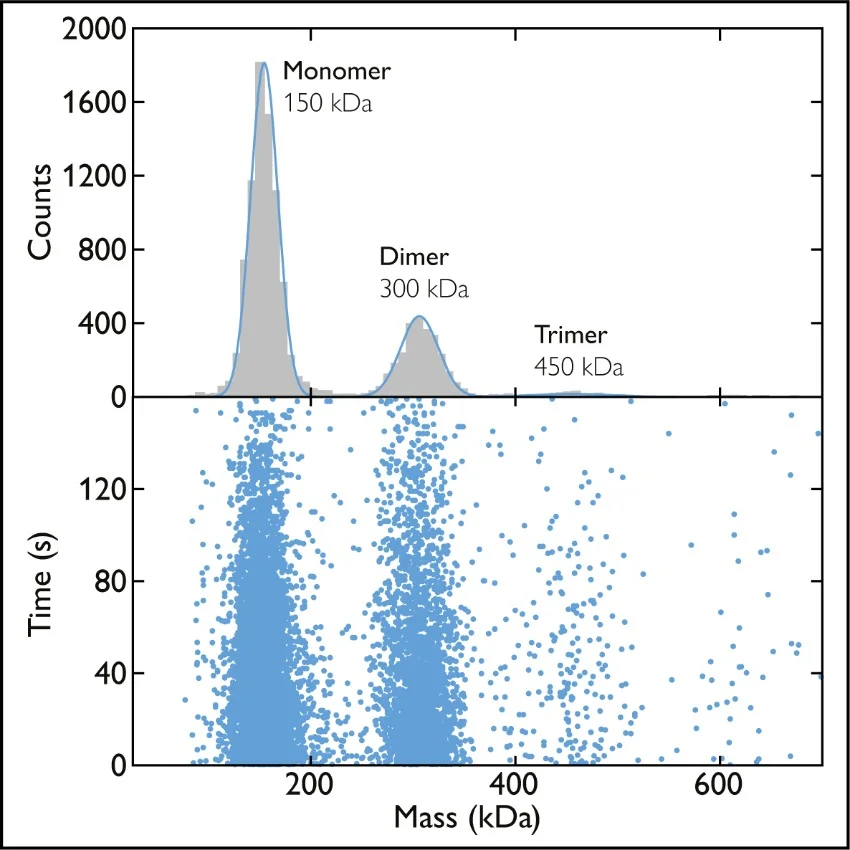
Mass photometry is a novel way to measure the mass of biomolecules. It works by quantifying the light scattered by an individual molecule in solution, which is directly proportional to the molecule’s mass [1], [2] (read more about how mass photometry works).
The biologically important membrane proteins remain a challenging target for structural and functional studies, despite recent advances in biomolecular characterization capabilities. This is due to intrinsic difficulties in expressing, purifying and preparing membrane proteins for analysis while preserving their structure and activity.
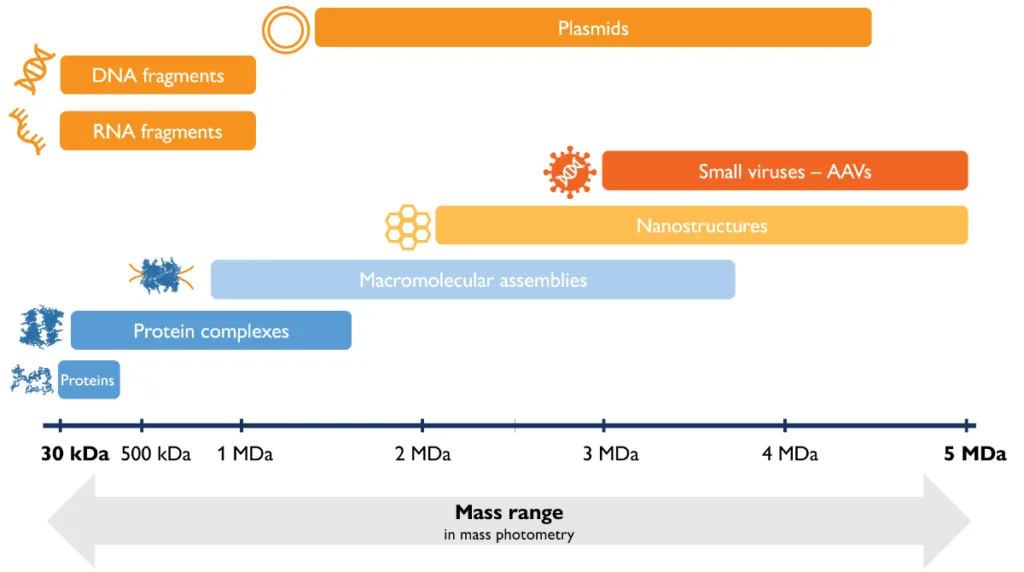
Mass photometry is an analytical method that measures molecular mass by quantifying light scattering from individual biomolecules in solution [1]. When considering mass photometry as a new technology for your lab, it is important to understand whether it is suitable for the types of samples you need to analyze.
Here, we describe mass photometry’s mass range, resolution and experimental error, the concentration ranges that can be analyzed, and other information you will find useful as you explore mass photometry.
Mass photometry is a novel bioanalytical technology that measures molecular mass by quantifying light scattering from individual biomolecules in solution




